The sharing economy has changed real estate, disrupting traditional business models and creating new opportunities for individuals to monetize their assets.
What is the sharing economy?
The sharing economy, also known as the collaborative economy or the gig economy, refers to the growing trend of individuals sharing or renting out their assets or services to others, often facilitated through digital platforms. This includes a wide range of activities such as home sharing through platforms like Airbnb, car sharing through platforms like Uber and Zipcar, and tools and equipment sharing through platforms like Rent the Runway and Zipcar.
The sharing economy has made it easier for people to earn extra money by renting out their properties, and it has also made it more affordable for travelers to find short-term accommodations in cities around the world. However, the rise of the sharing economy has also led to concerns about the impact on the housing market, as some worry that it could lead to an increase in rent prices and a decrease in the availability of affordable housing.
Despite these concerns, the sharing economy continues to grow and evolve, and it has already had a significant impact on the real estate industry. Keep reading to learn how the sharing economy has impacted the real estate market.
Co-working and effect on real estate
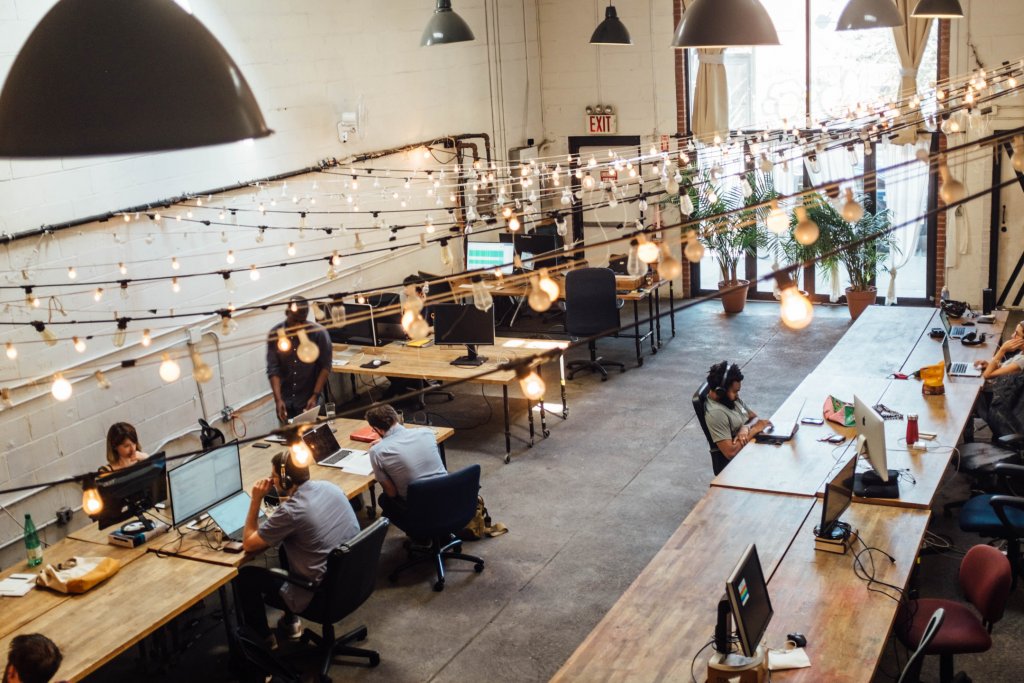

Co-working has had a significant impact on the real estate industry in recent years.
It refers to a style of work in which individuals from different companies or organizations share a common workspace, typically in a flexible and collaborative environment. Co-working spaces can range from small, informal gatherings to large, professional environments with a variety of amenities.
The benefits of co-working
One of the main benefits of co-working for real estate is the ability to fill unused or underutilized space.
Many traditional office buildings have excess capacity, and co-working allows landlords to monetize this space by renting it out to smaller businesses and entrepreneurs on a flexible basis. This can be especially appealing in areas where there is a high demand for office space but limited availability.
In addition to filling excess capacity, co-working can also help landlords attract new tenants.
By offering a co-working option, landlords can cater to a wider range of businesses and professionals, including freelancers, startups, and remote workers. This can help to increase the overall occupancy rate of a building and generate additional revenue.
Another benefit of co-working for real estate is the potential for increased property value.
Co-working spaces are often located in desirable locations, such as downtown areas or near transportation hubs. By hosting a co-working space, landlords can increase the value of their property by attracting businesses and professionals who are willing to pay a premium for access to these locations.
The challenges of co-working
There are also a number of challenges that the real estate industry has had to navigate in response to the rise of co-working.
One issue is the potential for increased competition among landlords. With more and more landlords offering co-working options, it can be difficult for individual properties to stand out in the market. Additionally, there is the risk that co-working could lead to an oversaturation of office space, which could drive down rental rates and reduce the overall value of properties.
Another challenge is the potential impact on traditional tenant-landlord relationships.
Co-working spaces operate on a different business model than traditional office leasing, with a focus on flexibility and short-term rentals. This can create uncertainty for landlords, who may be used to long-term tenants with more predictable revenue streams.
Despite these challenges, the impact of co-working on the real estate industry has largely been positive. It has provided landlords with new opportunities to monetize excess capacity and attract a wider range of tenants, and has helped to drive innovation and collaboration in the workplace. While there are certainly challenges to navigate, the growth of co-working is likely to continue, and real estate professionals will need to adapt to this evolving landscape.
The impact of co-living in real estate
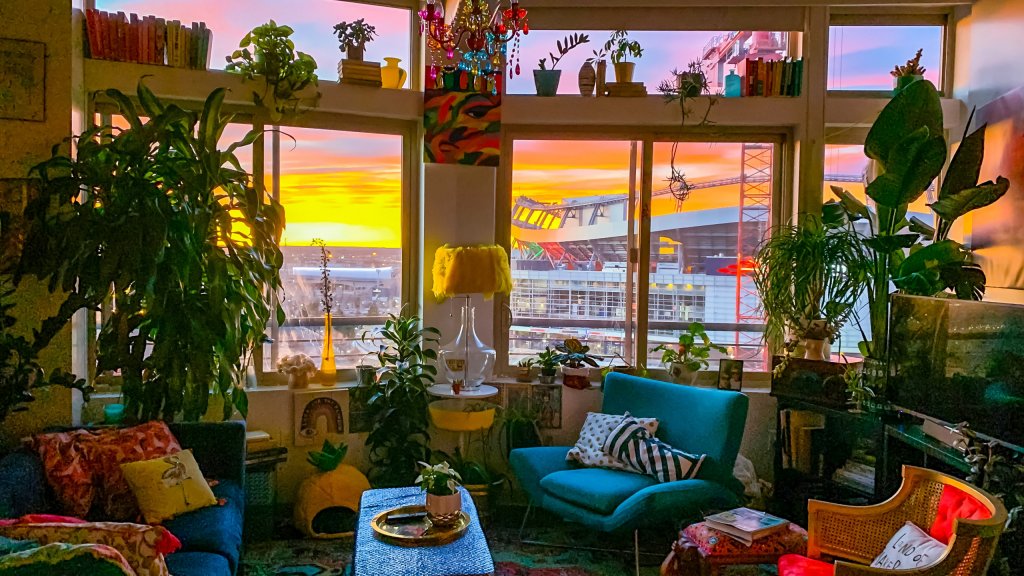

Co-living is a type of housing arrangement in which multiple people live together in a shared living space, typically with shared facilities such as a kitchen and common areas.
In recent years, the sharing economy has had a significant impact on the co-living industry, leading to the emergence of new co-living spaces and business models that take advantage of the sharing economy.
One of the main ways in which the sharing economy has impacted co-living is by making it more affordable.
Co-living spaces often offer a more affordable alternative to traditional apartments, as residents can split the cost of rent, utilities, and other expenses. In addition, the sharing economy allows residents to share resources such as appliances and furniture, which can further reduce the cost of living. For example, a co-living space might have a shared kitchen with multiple refrigerators and stoves, allowing residents to save money on appliances and energy costs.
The pros of co-living
The sharing economy has also made it easier for individuals to find co-living arrangements.
With the rise of online platforms such as Airbnb and Co-Living, it has become easier for people to search for and book co-living spaces. These platforms allow individuals to browse listings, read reviews, and communicate with potential roommates before committing to a co-living arrangement. This has made it easier for people to find co-living spaces that fit their budget and lifestyle, as well as to connect with like-minded individuals who are looking for a shared living situation.
In addition to making co-living more affordable and accessible, the sharing economy has also led to the development of new co-living business models.
For example, some co-living spaces are designed to cater to specific groups of people, such as digital nomads, students, or professionals. These spaces may offer additional amenities and services, such as co-working spaces, gym memberships, or social events, to attract a particular type of tenant. The sharing economy has also given rise to co-living spaces that are focused on sustainability and social responsibility, such as eco-friendly co-living communities or co-living spaces that donate a portion of their profits to charity.
The cons of co-living
One potential downside of the sharing economy’s impact on co-living is that it may lead to a lack of regulation and oversight in the industry.
Many co-living spaces operate on a short-term basis, with residents coming and going on a regular basis. This can make it difficult for local governments to regulate and inspect these spaces, which may result in safety and health concerns for residents. In addition, the sharing economy has been criticized for contributing to the gentrification of certain neighborhoods, as co-living spaces may attract higher-income residents and drive up rent prices in the area.
Overall, the sharing economy has had a significant impact on the co-living industry, making it more affordable, accessible, and diverse. While there are potential downsides to this trend, the sharing economy has also created new opportunities for individuals to find affordable and flexible housing options that meet their needs and interests. As the sharing economy continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how it continues to shape the co-living industry in the future.
Shared storage and the impact on real estate

The sharing economy has had a significant impact on the storage industry in recent years.
With the rise of platforms such as Airbnb and Uber, more and more people are turning to the sharing economy as a way to make extra money or save money on services and products. This trend has also extended to the storage industry, with the emergence of companies that allow individuals and businesses to rent out their unused storage space to others.
The positive side of shared storage
One of the main benefits of the sharing economy for storage is that it allows individuals and businesses to monetize their unused storage space.
Many people have extra space in their garages, basements, or attics that they are not using, and by renting out this space through a sharing economy platform, they can earn some extra income. Similarly, businesses that have excess warehouse or storage space can also use the sharing economy to generate additional revenue.
Another benefit of the sharing economy for storage is that it provides a more flexible and cost-effective solution for individuals and businesses in need of storage.
Traditional storage facilities can be expensive and inflexible, requiring long-term contracts and often charging high fees for access or late payments. In contrast, sharing economy storage solutions are often more flexible and offer more reasonable prices, allowing individuals and businesses to only pay for the storage they need, when they need it.
The sharing economy has also made it easier for people to find storage solutions in locations where traditional storage facilities may not be available or may be too expensive.
For example, individuals living in urban areas may have limited space for storage and may have to pay premium prices for storage solutions. The sharing economy allows them to find storage solutions in nearby neighborhoods or suburbs, where storage space may be more readily available and at a lower cost.
The negative side of shared storage
However, the sharing economy has also faced some challenges in the storage industry.
One concern is the lack of regulation and oversight of sharing economy storage solutions. Traditional storage facilities are subject to certain regulations and standards, such as security measures, insurance requirements, and health and safety standards. Sharing economy storage solutions may not be subject to the same regulations, which can raise concerns about the safety and security of stored items.
Another challenge is the lack of standardization in sharing economy storage solutions.
While traditional storage facilities often offer a range of unit sizes and services, sharing economy storage solutions can vary significantly in terms of the type and quality of storage space available. This can make it difficult for individuals and businesses to determine the best storage solution for their needs.
The sharing economy has had a significant impact on the storage industry, offering a more flexible and cost-effective solution for individuals and businesses in need of storage. However, it has also raised some concerns about regulation and standardization.
The sharing economy has disrupted hospitality

The sharing economy has had a significant impact on the hospitality industry in recent years, with companies like Airbnb and HomeAway revolutionizing the way people travel and find accommodations.
One of the most well-known examples of the sharing economy in the hospitality industry is Airbnb, a platform that allows individuals to list their homes or apartments as short-term rentals. Since its founding in 2008, Airbnb has grown rapidly and now has over 4 million listings in more than 100,000 cities around the world. The company’s success has led to the emergence of numerous similar platforms, such as HomeAway, VRBO, and FlipKey, which offer similar services.
Competition for hotels
The sharing economy has had a number of impacts on the hospitality industry. One of the most significant is the disruption of traditional hotel and accommodation businesses. Airbnb and other home-sharing platforms have provided an alternative to traditional hotels, particularly for travelers looking for a more authentic and local experience. This has led to increased competition for traditional hotels, as well as a shift in the way that travelers think about accommodation.
With the sharing economy, everyone can own a ‘hotel’
Another impact of the sharing economy in the hospitality industry is the democratization of the travel industry. Prior to the rise of platforms like Airbnb, it was difficult for individuals to enter the market as a host or a provider of accommodation. Now, anyone with a spare room or a vacation home can easily list it on Airbnb or a similar platform and begin earning income from it. This has led to a significant increase in the number of people participating in the sharing economy as hosts or providers of accommodation.
The plus side for travelers & hosts
One major benefit of the sharing economy for travelers is the increased availability of unique and affordable accommodation options. Traditional hotels can be expensive and cookie-cutter, but with the sharing economy, travelers have access to a wide variety of options ranging from cozy apartments to entire houses. This has made travel more accessible for many people, particularly for those on a budget or those who are looking for more authentic and local experiences. For hosts, the sharing economy has provided a new source of income and a way to monetize underutilized assets such as a spare bedroom or vacation home. It has also allowed them to interact with a global audience and showcase their community to visitors.
Concerns for safety and security
The sharing economy has not been without controversy, however. One of the main criticisms is that it is unregulated and that it allows individuals and companies to operate outside of the traditional regulatory framework. This has led to concerns about safety, security, and the rights of workers in the sharing economy. There have also been concerns about the impact on local communities, as the rise of home-sharing platforms has led to a decrease in the availability of long-term rental housing, which can be detrimental to local residents.
A decline in hotel revenue
However, the sharing economy has also brought some challenges for the hospitality industry. Traditional hotels have struggled to compete with the lower prices and increased availability offered by home-sharing platforms. This has led to a decline in hotel revenue and occupancy rates in some markets, as well as job losses for hotel employees.
The impact on local communities
There are also concerns about the impact of the sharing economy on the local housing market. In some cities, the influx of short-term rentals through platforms like Airbnb has contributed to rising housing costs and a decrease in the availability of long-term rentals for residents. This has led to calls for stricter regulations on home-sharing platforms and the creation of laws that balance the needs of hosts, guests, and the local community.
Lack of regulation and quality control
Another issue is the lack of consistency in terms of regulation and quality control in the sharing economy. Traditional hotels are subject to strict health and safety regulations and quality standards, but these standards may not apply to all home-sharing properties. This can lead to concerns about the safety and cleanliness of accommodations, and there have been instances of hosts taking advantage of the lack of oversight to engage in fraudulent or illegal activities.
The sharing economy has had a significant impact on the hospitality industry, particularly in the areas of accommodation and transportation. It has disrupted traditional businesses and has provided new opportunities for individuals to enter the market as hosts or providers of services. However, it has also faced criticism and regulatory challenges.
Despite these challenges, the sharing economy is here to stay and is likely to continue to grow and evolve. The hospitality industry will need to adapt to this new way of traveling and find ways to coexist with and even leverage the sharing economy. This may involve traditional hotels embracing home-sharing platforms and offering similar services, or it may involve the creation of new hybrid models that combine the best aspects of both. Ultimately, the success of the sharing economy in the hospitality industry will depend on the ability to strike a balance between the needs of all stakeholders and the creation of fair and sustainable policies.
Ride sharing competes with taxis
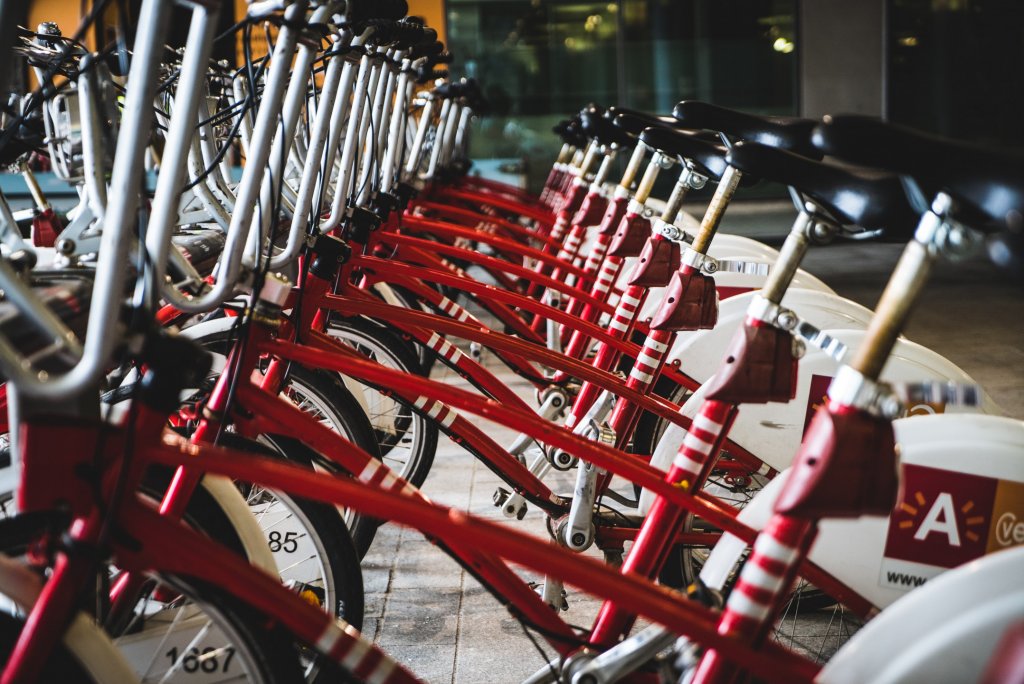

The sharing economy has also had an impact on the transportation industry within the hospitality sector.
Ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft have allowed individuals to use their personal vehicles to provide transportation services to others. These platforms have grown rapidly in recent years and now operate in cities around the world. Like home-sharing platforms, ride-sharing platforms have disrupted traditional taxi and transportation companies and have led to increased competition in the industry.
Conclusion

The sharing economy has had a significant impact on the real estate industry. It has given individuals the ability to monetize their underutilized assets, such as their homes or vehicles, and has created new opportunities for people to earn income. The popularity of home-sharing platforms like Airbnb has allowed people to rent out their homes or spare rooms to travelers, potentially generating significant income.
However, the sharing economy has also had some negative effects on the real estate industry. Some critics argue that it has contributed to the tight housing markets in certain cities, making it more difficult for people to find affordable housing. Additionally, the rise of the sharing economy has raised concerns about the impact on traditional rental businesses, as well as issues around regulation and taxation.
To conclude, the sharing economy has had a complex and multifaceted impact on the real estate industry, with both positive and negative effects.
It remains to be seen what the long-term effects of this trend will be, but it is clear that the sharing economy is here to stay and will continue to shape the way we think about and use our homes and other properties.